USB Drive Not Recognizing? This blog is just right for you!
Highlight before Troubleshooting
- Ensure you have Administrative Privileges: diskpart requires administrative permissions to run. Ensure you access your Windows as the primary or admin user, running the command prompt as an administrator.
- Check Disk Connection: This method will not work if the thumb drive is undetectable by Windows. If it is undetectable, check out this link to ensure Windows detects and recognizes it.If it is still undetectable, maybe the drive's chips are faulty. Just change to a new USB drive if your data is not important. Otherwise, seek a professional data recovery service centre to retrieve data.
- Double-Check Disk Selection: This method will delete all data from the selected drive. Always verify that you selected the correct disk before performing operations to avoid losing data.
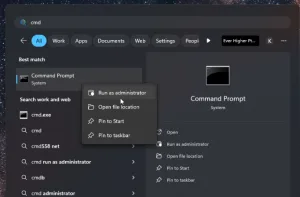
Open Command Prompt as Administrator
Search for "CMD" in the "Search" section beside the "Start" button. Right-click and select "Run As Administrator". This ensures you have the necessary permissions to manage disks.

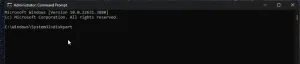
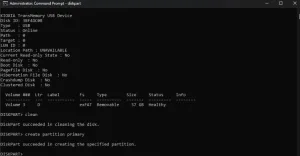
Start diskpart
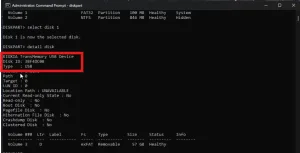
List All Disks
Then, insert "list disk" to view all the available drives connected to your computer. It will display all drives in their respective sizes and statuses. The drive will be shown as Disk 0, Disk 1, etc.
Select a Disk
Identify which Disk number is your thumb drive by looking at the data sizes. If you are unsure, you may check through them one by one like. Insert "select disk 1", hit "enter", and insert "detail disk" and look for USB type.

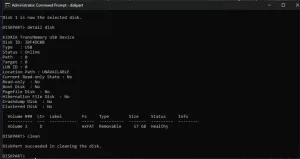
Clean the Disk
After selecting the disk number, insert "clean". At this stage, it will erase everything on the drive. That is why selecting the correct disk number is very important.

Create a New Partition
After completing, insert "create partition primary." This command will allocate all available space to the new partition.

Format the Partition
Then, format the created partition with the file system you want by inserting "format fs=Y quick." Replace the Y with the file system you need.
NTFS: The drive is viewable in Windows and MacOS, but you can't edit the file on Mac. (format fs=ntfs quick)
Exfat: The drive is usable on Windows and MacOS. (format fs=exfat quick)
Fat32: The drive is usable on Windows and MacOS, but it limits the size of each file to 4 GB and below.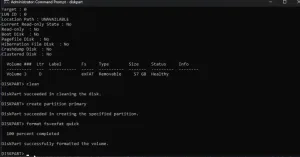
Exit diskpart
Once you've completed your tasks, close your CMD.
Conclusion
Diskpart is a versatile tool for managing disks and partitions, allowing you to perform operations directly from the command line. While it is powerful, it also requires careful handling to avoid unintentional data loss. Always double-check commands and ensure backups are available before proceeding with operations that modify disk data.